Using report templates to monitor hosts
You can use report templates to query orcharhino data to obtain information about, for example, host status, registered hosts, applicable errata, applied errata, and user activity. You can use the report templates that ship with orcharhino or write your own custom report templates to suit your requirements. The reporting engine uses the embedded Ruby (ERB) syntax. For more information about writing templates and ERB syntax, see Template Writing Reference.
You can create a template, or clone a template and edit the clone. For help with the template syntax, click a template and click the Help tab.
Writing Report Templates
Report templates are ruby scripts executed on orcharhino itself and able to extract, process, and present information from internal databases in a tabular form. They represent an easy way within orcharhino to generate customizable reports. This guide describes how to write and modify report templates.
orcharhino already contains a selection of generic report templates. Navigate to Monitor > Report Templates:
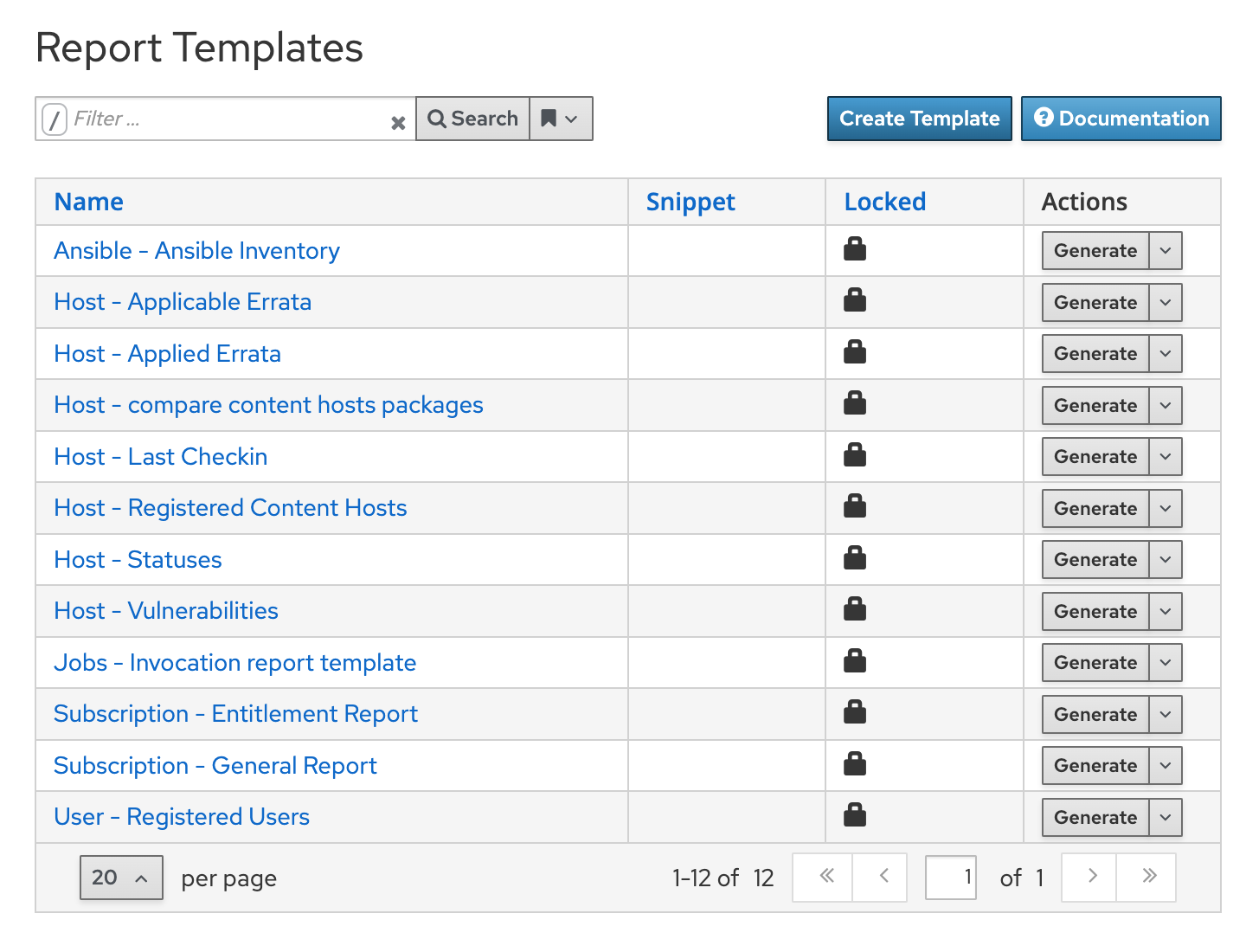
As an example, this guide shows you how to write a template, which returns the number and kind of installable errata on managed hosts. Errata contain information to update and/or patch software. They cover security updates, bugfixes, or new software features. For this purpose, every erratum contains a list of packages affected by the update. Keeping a watchful eye on errata is therefore always a good idea to keep your hosts up to date. In this context, orcharhino distinguishes between two types of errata, installable and available errata:
-
Available errata for a host are always determined with respect to the latest packages maintained by the orcharhino.
-
Available errata may differ from installable errata, as hosts are normally registered to a frozen state of packages, so called content views.
The final template shows both the number of applicable and installable errata for each host.
Report Template for Applicable Errata
You can create a report template to return a short summary of all errata affected hosts. It focuses on applicable errata first.
The new report is generated by selecting the corresponding button on the Monitor > Report Templates page. Then, the template name and some generic information like the template category, a collection of templates with similar purpose, are added as well as the template code:
<%#
name: Applicable Errata
description: A basic report template for gathering all applicable errata.
model: ReportTemplate
-%>
<%# Loop over all hosts-%>
<%- load_hosts(includes: [:operatingsystem, :applicable_errata, :lifecycle_environment]).each_record do |host| -%>
<%- @errata = 0 -%>
<%- if host.operatingsystem.family != "Windows" -%>
<%- # Loop over all errata for the single host -%>
<%- host_applicable_errata_filtered(host).each do |erratum| -%>
<%- @errata = @errata+1 -%>
<%- end -%>
<%- report_row(
'Host': host.name,
'OS': host.operatingsystem,
'Environment': host.lifecycle_environment,
'Total': @errata,
) -%>
<%- end -%>
<%- end -%>
<%= report_render -%>The first part of the code from line 1 to 5 is a commentary block, indicated by the brackets <%# … -%>.
This block contains metadata like the template name and its description.
The first executable Ruby code starts in line 7, marked by the brackets <%- -%>.
The macro load_hosts in this line loads the host data contained in the orcharhino.
Which information it exactly processes is determined by the includes keyword.
In this case, these are the operating system, the lifecycle environment, and the applicable errata.
In typical ruby-style, the following each_record do |host| iterates over all returned hosts entries saved in host.
Windows hosts are explicitly excluded from the host list in line 9.
The applicable errata for each Linux host are then processed via the host_applicable_errata_filtered() macro in line 11.
The exact number of applicable errata is then summed up in the counter @errata and passed to the report_row() macro in line 14.
This macro adds a corresponding host line to the report table, which is then rendered via <%= report\_render -%> at the end of the template.
After defining the template can now be executed by hitting the Generate button below the template in the web GUI.
The appearing interface requires some additional information like the execution time and date, the file format (csv, json, yaml, html), and mail forwarding.
The template is now executed, returns a table in the csv-format, and uses no mail forwarding.
The final report looks like this:
| Host | OS | Environment | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
centos9.example.com |
CentOS 9 |
Testing |
32 |
oracle9.example.com |
OracleLinux 9 |
Testing |
163 |
debian10.example.com |
Debian 10 |
Testing |
23 |
Every row of the table represents one host with some basic information and the total available errata count. This short and easy to read table now serves as a basis for further enhancement of the template.
Errata Types
Extend the template with two additional features: First, allow users to restrict the report to a list of selected hosts instead of all hosts and second, display the kind of errata in the report. The modified template looks as follows:
<%#
name: Applicable Errata
description: A basic report template for gathering all applicable errata.
template_inputs:
- name: Hosts filter
required: false
input_type: user
advanced: false
value_type: plain
hidden_value: false
model: ReportTemplate
-%>
<%# Loop over all or input list of hosts -%>
<%- load_hosts(search: input('Hosts filter'), includes: [:operatingsystem, :applicable_errata, :lifecycle_environment]).each_record do |host| -%>
<%- if host.operatingsystem.family != "Windows" -%>
<%- @errata = 0 -%>
<%- @bugfix = 0 -%>
<%- @misc_err = 0 -%>
<%- @enhancement = 0 -%>
<%- @security = 0 -%>
<%- # Loop over all errata for the single host -%>
<%- host_applicable_errata_filtered(host).each do |erratum| -%>
<%- @errata = @errata+1 -%>
<%- if erratum[:errata_type]=="security" -%>
<%- @security=@security+1 -%>
<%- elsif erratum[:errata_type]=="bugfix" -%>
<%- @bugfix=@bugfix+1 -%>
<%- elsif erratum[:errata_type]=="recommended" -%>
<%- @bugfix=@bugfix+1 -%>
<%- elsif erratum[:errata_type]=="enhancement" -%>
<%- @enhancement=@enhancement+1 -%>
<%- elsif erratum[:errata_type]=="optional" -%>
<%- @enhancement=@enhancement+1 -%>
<%- else -%>
<%- @misc_err=@misc_err+1 -%>
<%- end -%>
<%- end -%>
<%- report_row(
'Host': host.name,
'OS': host.operatingsystem,
'Environment': host.lifecycle_environment,
#Library specific errata
'Security': @security,
'Bugfix': @bugfix,
'Enhance': @enhancement,
'Misc': @misc_err,
'Total': @errata,
) -%>
<%- end -%>
<%- end -%>
<%= report_render -%>load_hosts in line 14 is now extended by search: input('Hosts filter').
The macro input allows users to add input during execution of the template.
In this case, it limits the search to a list of hosts.
To let this macro take effect, add the input name Hosts filter to the Inputs tab of the template:
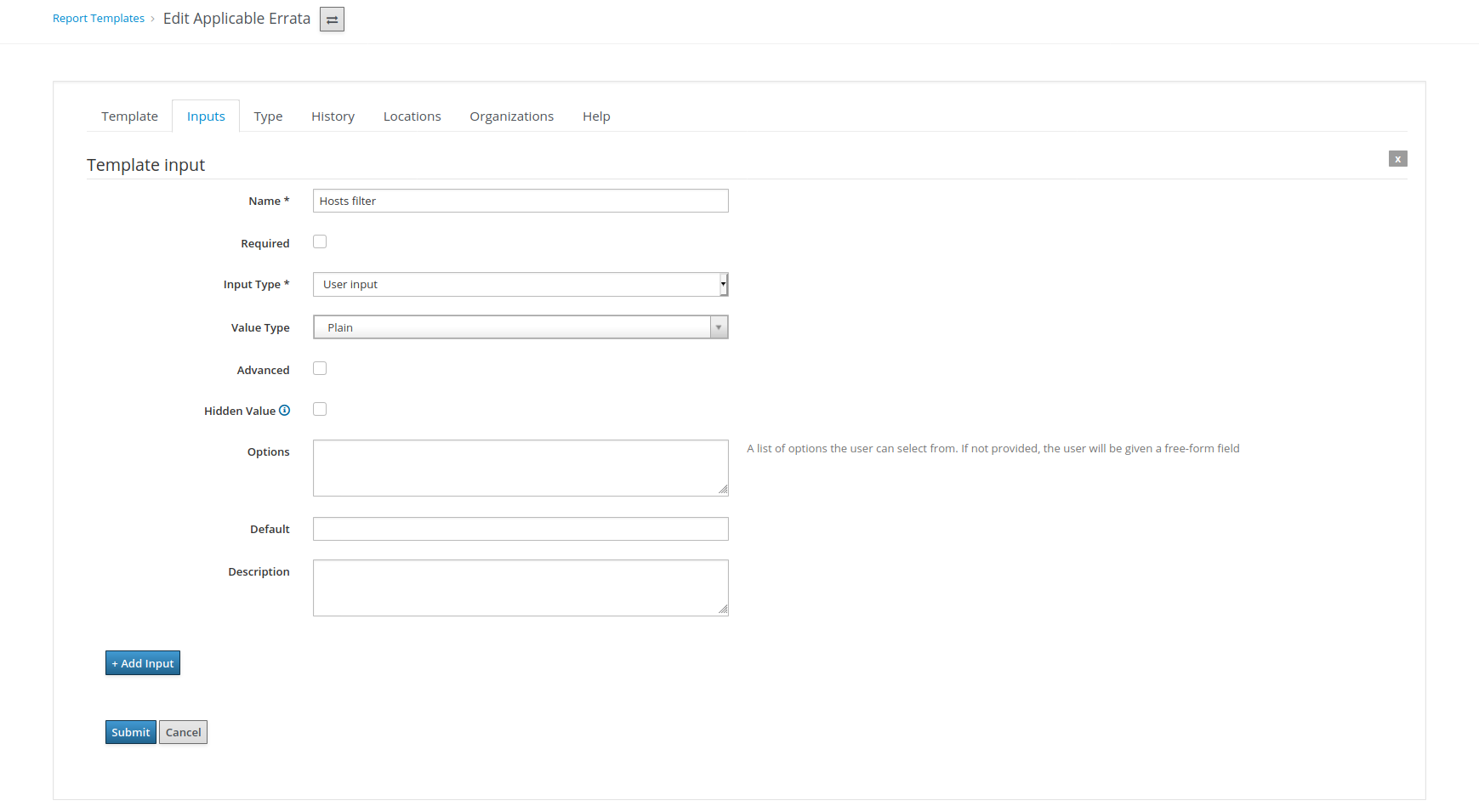
Additionally, the template now distinguishes between security, bugfix, and enhancement errata. The corresponding counters are defined in line 16 to 20 and count for the erratum kind in line 22 to 36 via an if-clause.
The user generating the report now has one additional field Hosts filter available:
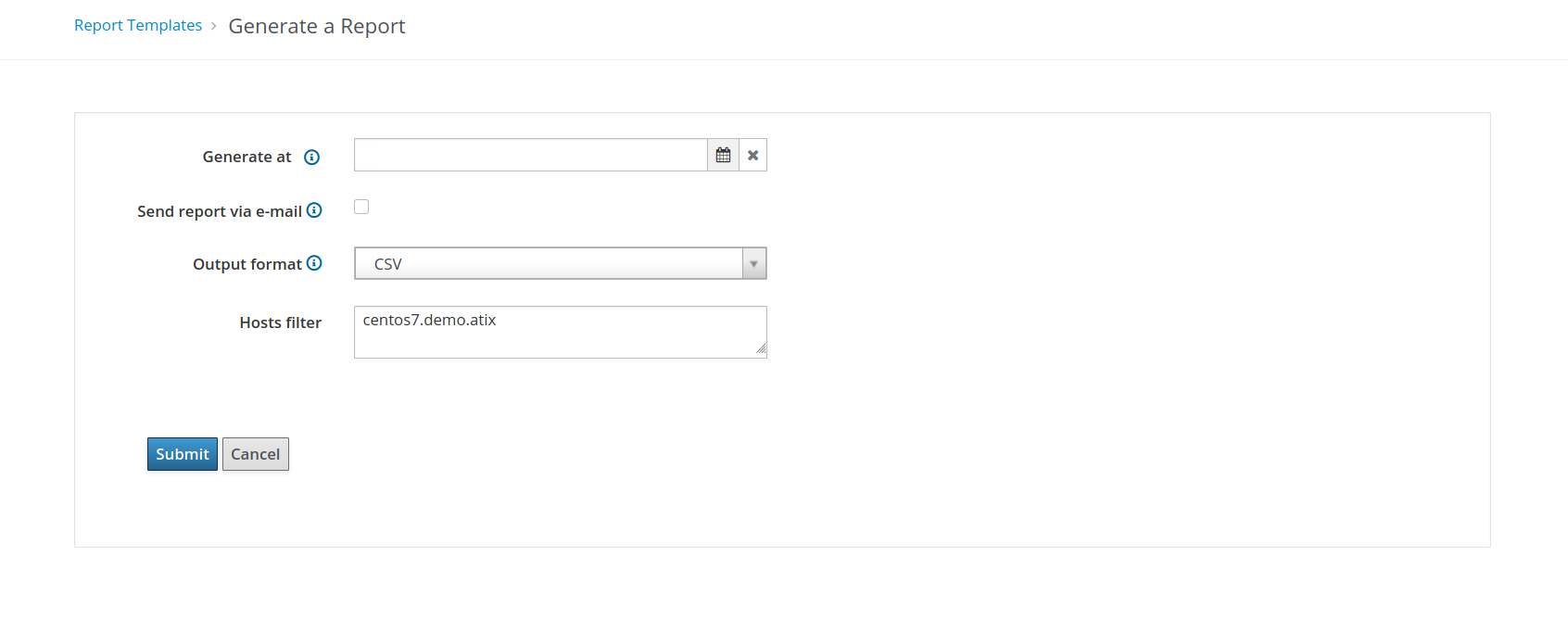
The output for the centos9.example.com host looks as follows:
| Host | OS | Environment | Security | Bugfix | Enhance | Misc | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
centos9.example.com |
CentOS 9 |
Testing |
9 |
20 |
2 |
1 |
32 |
Nine of the applicable errata are in fact security errata, a definite warning sign to patch the host as soon as possible.
Installable vs Available Errata
We still do not know if these errata are also installable on the host and how many packages are indeed affected by available errata. We therefore modify the template one final time:
<%#
name: Applicable Errata
description: A basic report template for gathering all applicable errata.
template_inputs:
- name: Hosts filter
required: false
input_type: user
advanced: false
value_type: plain
hidden_value: false
model: ReportTemplate
-%>
<%# Loop over all or input list of hosts -%>
<%- load_hosts(search: input('Hosts filter'), includes: [:operatingsystem, :applicable_errata, :lifecycle_environment]).each_record do |host| -%>
<%- if host.operatingsystem.family != "Windows" -%>
<%- @errata = 0 -%>
<%- @bugfix = 0 -%>
<%- @misc_err = 0 -%>
<%- @enhancement = 0 -%>
<%- @security = 0 -%>
<%- #Content View Errata%>
<%- @cv_misc_err = host.content_facet_attributes.errata_counts[:total] -%>
<%- @cv_misc_err = @cv_misc_err - host.content_facet_attributes.errata_counts[:enhancement] -%>
<%- @cv_misc_err = @cv_misc_err - host.content_facet_attributes.errata_counts[:bugfix] -%>
<%- @cv_misc_err = @cv_misc_err - host.content_facet_attributes.errata_counts[:security] -%>
<%- # Loop over all errata for the single host -%>
<%- host_applicable_errata_filtered(host).each do |erratum| -%>
<%- @errata = @errata+1 -%>
<%- if erratum[:errata_type]=="security" -%>
<%- @security=@security+1 -%>
<%- elsif erratum[:errata_type]=="bugfix" -%>
<%- @bugfix=@bugfix+1 -%>
<%- elsif erratum[:errata_type]=="recommended" -%>
<%- @bugfix=@bugfix+1 -%>
<%- elsif erratum[:errata_type]=="enhancement" -%>
<%- @enhancement=@enhancement+1 -%>
<%- elsif erratum[:errata_type]=="optional" -%>
<%- @enhancement=@enhancement+1 -%>
<%- else -%>
<%- @misc_err=@misc_err+1 -%>
<%- end -%>
<%- end -%>
<%- report_row(
'Host': host.name,
'OS': host.operatingsystem,
'Environment': host.lifecycle_environment,
#Library specific errata
'Security': @security,
'Bugfix': @bugfix,
'Enhance': @enhancement,
'Misc': @misc_err,
'Total': @errata,
#Content View specific errata
'CV Security': host.content_facet_attributes.errata_counts[:security],
'CV Bugfix': host.content_facet_attributes.errata_counts[:bugfix],
'CV Enhance': host.content_facet_attributes.errata_counts[:enhancement],
'CV Misc': @cv_misc_err,
'CV Total': host.content_facet_attributes.errata_counts[:total],
'Packages': host.content_facet_attributes.applicable_deb_count+host.content_facet_attributes.applicable_rpm_count,
) -%>
<%- end -%>
<%- end -%>
<%= report_render -%>We now access the number of installable errata via the host attribute host.content_facet_attributes.errata_counts.
Additionally, we save the number of errata belonging to none of the predefined categories in the counter @cv_misc_err.
We then return the installable errata counts from line 55 to 59.
The report for host centos9.example.com then looks like this:
| Host | OS | Environment | Security | Bugfix | Enhance | Misc | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
centos9.example.com |
CentOS 9 |
Testing |
9 |
20 |
2 |
1 |
32 |
| Host | CV Security | CV Bugfix | CV Enhance | CV Misc | CV Total | Packages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
centos9.example.com |
6 |
13 |
1 |
0 |
20 |
242 |
We now see that the number of installable errata is smaller than the number of available errata. Ensure to update the corresponding content view as soon as possible.
Report templates allow access to all functionalities of the orcharhino API and orcharhino intern variables. For more information, see Template Writing Reference.
Generating host monitoring reports
To view the report templates in the orcharhino management UI, navigate to Monitor > Reports > Report Templates. To schedule reports, configure a cron job or use the orcharhino management UI.
-
In the orcharhino management UI, navigate to Monitor > Reports > Report Templates. For example, the Host – Installed Products template generates a report with installed product information along with other metrics, including system purpose attributes.
-
To the right of the report template that you want to use, click Generate.
-
Optional: To schedule a report, to the right of the Generate at field, click the icon to select the date and time you want to generate the report at.
-
Optional: To send a report to an e-mail address, select the Send report via e-mail checkbox, and in the Deliver to e-mail addresses field, enter the required e-mail address.
-
Optional: Apply search query filters. To view all available results, do not populate the filter field with any values.
-
Click Submit. A CSV file that contains the report is downloaded. If you have selected the Send report via e-mail checkbox, the host monitoring report is sent to your e-mail address.
-
List all available report templates:
$ hammer report-template list -
Generate a report:
$ hammer report-template generate --id My_Template_IDThis command waits until the report fully generates before completing. If you want to generate the report as a background task, you can use the
hammer report-template schedulecommand.If you want to generate the Subscription - General report, you have to use the
Days from Nowoption to specify the latest expiration time of general subscriptions.Show all subscriptions$ hammer report-template generate \ --inputs "Days from Now=no limit" \ --name "Subscription - General Report"Show all subscriptions that are going to expire within 60 days$ hammer report-template generate \ --inputs "Days from Now=60" \ --name "Subscription - General Report"
Creating a report template
In orcharhino, you can create a report template and customize the template to suit your requirements. You can import existing report templates and further customize them with snippets and template macros.
Report templates use Embedded Ruby (ERB) syntax. To view information about working with ERB syntax and macros, in the orcharhino management UI, navigate to Monitor > Reports > Report Templates, and click Create Template, and then click the Help tab.
When you create a report template in orcharhino, safe mode is enabled by default.
-
In the orcharhino management UI, navigate to Monitor > Reports > Report Templates.
-
Click Create Template.
-
In the Name field, enter a unique name for your report template.
-
If you want the template to be available to all locations and organizations, select Default.
-
Create the template directly in the template editor or import a template from a text file by clicking Import. For more information about importing templates, see Importing Report Templates.
-
Optional: In the Audit Comment field, you can add any useful information about this template.
-
Click the Input tab, and in the Name field, enter a name for the input that you can reference in the template in the following format:
input('name'). Note that you must save the template before you can reference this input value in the template body. -
Select whether the input value is mandatory. If the input value is mandatory, select the Required checkbox.
-
From the Value Type list, select the type of input value that the user must input.
-
Optional: If you want to use facts for template input, select the Advanced checkbox.
-
Optional: In the Options field, define the options that the user can select from. If this field remains undefined, the users receive a free-text field in which they can enter the value they want.
-
Optional: In the Default field, enter a value, for example, a host name, that you want to set as the default template input.
-
Optional: In the Description field, you can enter information that you want to display as inline help about the input when you generate the report.
-
Optional: Click the Type tab, and select whether this template is a snippet to be included in other templates.
-
Click the Location tab and add the locations where you want to use the template.
-
Click the Organizations tab and add the organizations where you want to use the template.
-
Click Submit to save your changes.
-
For more information about safe mode, see Report Template Safe Mode.
-
For more information about writing templates, see Template Writing Reference.
-
For more information about macros you can use in report templates, see Template Macros.
Exporting report templates
You can export report templates that you create in orcharhino.
-
In the orcharhino management UI, navigate to Monitor > Reports > Report Templates.
-
Locate the template that you want to export, and from the list in the Actions column, select Export.
-
Repeat this action for every report template that you want to download.
An .erb file that contains the template downloads.
-
To view the report templates available for export, enter the following command:
$ hammer report-template listNote the template ID of the template that you want to export in the output of this command.
-
To export a report template, enter the following command:
$ hammer report-template dump --id My_Template_ID > example_export.erb
Exporting report templates using the orcharhino API
You can use the orcharhino report_templates API to export report templates from orcharhino.
-
Use the following request to retrieve a list of available report templates:
Example request:$ curl --insecure --user admin:redhat \ --request GET \ --config https://orcharhino.example.com/api/report_templates \ | json_reformatIn this example, the
json_reformattool is used to format the JSON output.Example response:{ "total": 6, "subtotal": 6, "page": 1, "per_page": 20, "search": null, "sort": { "by": null, "order": null }, "results": [ { "created_at": "2019-11-20 17:49:52 UTC", "updated_at": "2019-11-20 17:49:52 UTC", "name": "Applicable errata", "id": 112 }, { "created_at": "2019-11-20 17:49:52 UTC", "updated_at": "2019-11-20 17:49:52 UTC", "name": "Applied Errata", "id": 113 }, { "created_at": "2019-11-30 16:15:24 UTC", "updated_at": "2019-11-30 16:15:24 UTC", "name": "Hosts - complete list", "id": 158 }, { "created_at": "2019-11-20 17:49:52 UTC", "updated_at": "2019-11-20 17:49:52 UTC", "name": "Host statuses", "id": 114 }, { "created_at": "2019-11-20 17:49:52 UTC", "updated_at": "2019-11-20 17:49:52 UTC", "name": "Registered hosts", "id": 115 }, { "created_at": "2019-11-20 17:49:52 UTC", "updated_at": "2019-11-20 17:49:52 UTC", "name": "Subscriptions", "id": 116 } ] } -
Note the
idof the template that you want to export, and use the following request to export the template:Example request:$ curl --insecure --output /tmp/_Example_Export_Template.erb_ \ --user admin:password --request GET --config \ https://orcharhino.example.com/api/report_templates/My_Template_ID/exportNote that
158is an example ID of the template to export.In this example, the exported template is redirected to
host_complete_list.erb.
Importing report templates
You can import a report template into the body of a new template that you want to create. Note that using the orcharhino management UI, you can only import templates individually. For bulk actions, use the orcharhino API. For more information, see Importing Report Templates Using the API.
-
You must have exported templates from orcharhino to import them to use in new templates. For more information see Exporting Report Templates.
-
In the orcharhino management UI, navigate to Monitor > Reports > Report Templates.
-
In the upper right of the Report Templates window, click Create Template.
-
On the upper right of the Editor tab, click the folder icon, and select the
.erbfile that you want to import. -
Edit the template to suit your requirements.
-
Click Submit.
For more information about customizing your new template, see Template Writing Reference.
Importing report templates using the orcharhino API
You can use the orcharhino API to import report templates into orcharhino. Importing report templates using the orcharhino API automatically parses the report template metadata and assigns organizations and locations.
-
Create a template using
.erbsyntax or export a template from another orcharhino.For more information about writing templates, see Template Writing Reference.
For more information about exporting templates from orcharhino, see Exporting Report Templates Using the API.
-
Use the following example to format the template that you want to import to a
.jsonfile:$ cat Example_Template.json { "name": "Example Template Name", "template": " Enter ERB Code Here " }Example JSON file with ERB template:{ "name": "Hosts - complete list", "template": " <%# name: Hosts - complete list snippet: false template_inputs: - name: host required: false input_type: user advanced: false value_type: plain resource_type: Katello::ActivationKey model: ReportTemplate -%> <% load_hosts(search: input('host')).each_record do |host| -%> <% report_row( 'Server FQDN': host.name ) -%> <% end -%> <%= report_render %> " } -
Use the following request to import the template:
$ curl --insecure --user admin:redhat \ --data @Example_Template.json --header "Content-Type:application/json" \ --request POST --config https://orcharhino.example.com/api/report_templates/import -
Use the following request to retrieve a list of report templates and validate that you can view the template in orcharhino:
$ curl --insecure --user admin:redhat \ --request GET --config https://orcharhino.example.com/api/report_templates | json_reformat
Generating a list of installed packages
Use this procedure to generate a list of installed packages in Report Templates.
-
In the orcharhino management UI, navigate to Monitor > Reports > Report Templates.
-
To the right of Host - All Installed Packages, click Generate.
-
Optional: Use the Hosts filter search field to search for and apply specific host filters.
-
Click Generate.
-
If the download does not start automatically, click Download.
-
You have the spreadsheet listing the installed packages for the selected hosts downloaded on your machine.
Report template safe mode
When you create report templates in orcharhino, safe mode is enabled by default. Safe mode limits the macros and variables that you can use in the report template. Safe mode prevents rendering problems and enforces best practices in report templates. The list of supported macros and variables is available in the orcharhino management UI.
To view the macros and variables that are available, in the orcharhino management UI, navigate to Monitor > Reports > Report Templates and click Create Template. In the Create Template window, click the Help tab and expand Safe mode methods.
While safe mode is enabled, if you try to use a macro or variable that is not listed in Safe mode methods, the template editor displays an error message.
To view the status of safe mode in orcharhino, in the orcharhino management UI, navigate to Administer > Settings and click the Provisioning tab. Locate the Safemode rendering row to check the value.
|
The text and illustrations on this page are licensed by ATIX AG under a Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 4.0 International ("CC BY-SA 4.0") license. This page also contains text from the official Foreman documentation which uses the same license ("CC BY-SA 4.0"). |